Publication
 HOME > Publications > Publication
HOME > Publications > Publication Thermal Fluctuation and Elasticity of Lipid Vesicles Interacting with Pore-forming Peptides Hit : 388
Ji-Hwan Lee, Sung-Min Choi, Changwoo Doe, Antonio Faraone, Phillip A. Pincus, and Steven R. Kline
105, 038101 (2010)
 http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.038101
http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.038101
Abstract
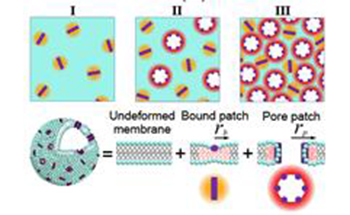
The thermal fluctuation and elasticity of dioleoyl-phosphocholine large unilamellar vesicle interacting with pore-forming peptide, melittin, were investigated by neutron spin-echo measurements. The relaxation behavior of the membrane fluctuation with different peptide to lipid molar ratio P/L
can be divided into three regions, resulting from characteristic changes of the effective bending modulus κ ˜
of the membrane which includes the effects of internal dissipation within the membrane. At low P/L
, melittin is adsorbed parallel to the surface of membrane and κ ˜
decreases significantly due to perturbation of hydrocarbon chain packing. At a critical P/L
, melittin forms pores in the membrane and κ ˜
starts to increase slightly due to high pore rigidity. At higher P/L
where the repulsive interpore interaction becomes significant, κ ˜
increases rapidly.
이지환 2010 350.jpg
105, 038101 (2010)
 http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.038101
http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.038101
Abstract

The thermal fluctuation and elasticity of dioleoyl-phosphocholine large unilamellar vesicle interacting with pore-forming peptide, melittin, were investigated by neutron spin-echo measurements. The relaxation behavior of the membrane fluctuation with different peptide to lipid molar ratio



