Fabrication of Nanoparticle Superlattice
 HOME > Research > Fabrication of Nanoparticle Superlattice
HOME > Research > Fabrication of Nanoparticle Superlattice Self-assembled superlattices that can be made using spherical or cylindrical nanoparticles as building blocks are highly demanded for realization of nano-technologies and various potential applications. Intrinsic properties of metallic and semiconducting nanoparticles can be coupled when they are put together into highly ordered superlattices, emerging the novel and synergetic properties of the superlattices. Although many methods for the fabrication of superlattices have been reported, further knowledge about more elegant and diverse morphologies of superlattices is required for the practical applications.
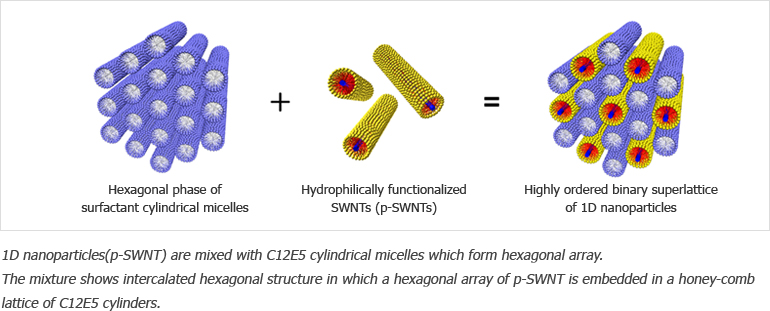
Until now, our group has learned that many interactions and their balance between repulsive and attractive interaction are the key parameters for the fabrication of superlattices and its morphologies. The highly ordered structures composed of single wall carbon nanotubes(SWNTs) or gold nanoparticles have been achieved using the electrostatic, hydrophobic, magnetic, chemical bonding, depletion, and other interaction. In addition, more complex and diverse symmetry of superlattices can be achieved from the mixture of dissimilar nanoparticles (Binary Superlattices). Thus, we are focusing on the fabrication of binary superlattices with different size or functionalities which may provide synergetic properties from the collective coupling.